Defining “First Quantum Stock Price”
Understanding the “first quantum stock price” requires clarifying what constitutes a “quantum” company and examining the historical context of quantum computing’s entry into the public market. This involves identifying the first publicly traded company significantly involved in quantum computing technologies and analyzing its initial stock performance.
Meaning of “First Quantum Stock Price”
In the stock market, the “first quantum stock price” refers to the initial price of a company’s stock at its Initial Public Offering (IPO) that is primarily focused on developing or commercializing quantum computing technologies. This represents a landmark moment, marking the entry of quantum computing into the realm of publicly traded investments. The historical context involves the gradual maturation of quantum computing technology from theoretical research to commercially viable applications, leading to the first company’s bold move to seek public funding.
Defining a “Quantum” Company
A “quantum” company in the investment world is one whose core business revolves around the development, manufacturing, or application of quantum computing technologies. This includes companies designing quantum processors, developing quantum algorithms, building quantum computers, or providing quantum computing-as-a-service. These companies are differentiated from those merely utilizing quantum computing principles in a secondary role. The definition is somewhat fluid, as the field is rapidly evolving.
Interpretations of “First”
The term “first” in this context is open to interpretation. It could refer to the chronologically first IPO of a company with significant involvement in quantum computing, or the first company to achieve a certain level of market capitalization or technological advancement within the sector. A more nuanced understanding requires considering the specific criteria used to define “first”.
Identifying the Relevant Company(ies)
Pinpointing the company with the “first quantum stock price” necessitates establishing clear criteria. This section identifies potential candidates, evaluating their technological contributions and market position at the time of their IPO. The criteria used include the primary focus of the company’s business on quantum computing, the significance of its technological advancements, and the timing of its IPO.
Potential Candidates and Criteria
Several companies could be considered candidates, depending on the specific criteria used. The key criteria are: the primary business focus on quantum computing, the maturity of their technology at IPO, and the market impact of their IPO. A thorough analysis requires considering both the technological advancements and the market context at the time of each company’s IPO.
Technological Advancements and Market Position
The companies considered should have demonstrated significant technological advancements in quantum computing at the time of their IPO. This might involve breakthroughs in qubit technology, algorithm development, or the creation of functional quantum computers. Their market position would also be a factor, considering their potential for growth and market share within the emerging quantum computing industry.
Table of Potential Candidates
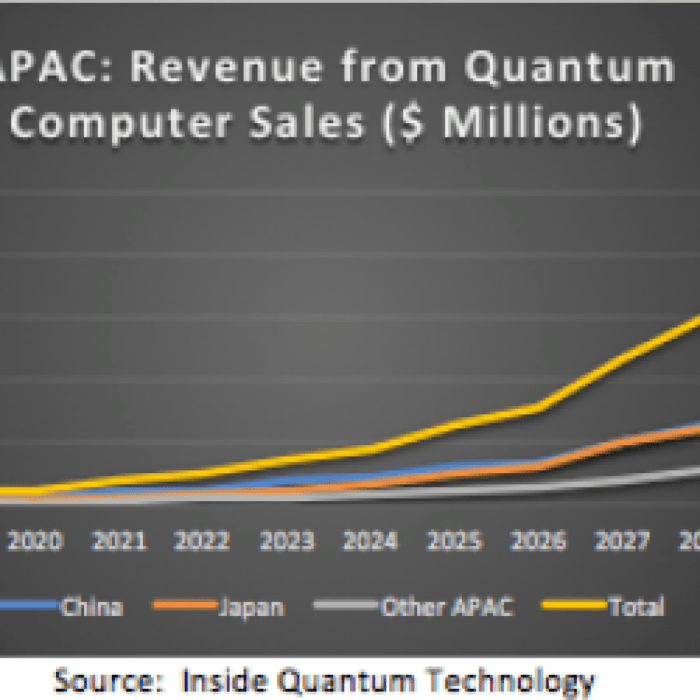
Source: insidequantumtechnology.com
| Company Name | Stock Ticker | IPO Date | Market Cap at IPO (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Example: IonQ) | (Example: IONQ) | (Example: October 2021) | (Example: $2 Billion) |
| (Example: Rigetti Computing) | (Example: RGTI) | (Example: August 2021) | (Example: $1.5 Billion) |
Analyzing Historical Stock Performance
Analyzing the historical stock price data of the identified companies provides insights into investor sentiment towards quantum computing and the factors influencing its valuation. This analysis will focus on identifying key trends and correlating them with technological advancements and broader market conditions.
Historical Stock Price Data
Examining the historical stock price data reveals patterns and trends that can help understand investor behavior and market dynamics. Specific data points, such as the initial price, highs, lows, and closing prices over time, are crucial for this analysis. The following table illustrates a sample data set; actual data should be sourced from reliable financial databases.
Determining the first quantum stock price is complex, as it depends on the specific company and its initial public offering. However, understanding the current market landscape is crucial; a good starting point might be checking the current price of IBM stock , a major player in quantum computing technology. This can provide some context for evaluating the potential valuation of other, newer quantum companies.
Table of Historical Stock Prices (Example)
| Date | Open Price (USD) | High Price (USD) | Close Price (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023-10-26 | 10.50 | 10.75 | 10.60 |
| 2023-10-27 | 10.65 | 11.00 | 10.85 |
Influencing Factors and Investor Sentiment
Fluctuations in stock prices are influenced by a multitude of factors, including technological breakthroughs (e.g., announcements of new algorithms or hardware advancements), macroeconomic conditions (e.g., interest rate changes, overall market sentiment), and investor speculation. Positive news regarding technological progress tends to boost investor confidence, while negative news or setbacks can lead to price drops.
The stock’s performance reflects the evolving perception of the quantum computing market’s potential and its associated risks.
Factors Influencing Stock Price
The stock price of a quantum computing company is a complex interplay of macroeconomic factors, technological progress, investor sentiment, and market trends. Understanding these influences is crucial for investors seeking to navigate this emerging sector.
Macroeconomic Factors
Broader economic conditions, such as interest rate hikes, inflation, and overall market volatility, significantly influence investor risk appetite. During periods of economic uncertainty, investors might shift away from riskier assets, including quantum computing stocks, impacting their prices. Conversely, periods of economic growth can lead to increased investment in these potentially high-reward sectors.
Technological Breakthroughs, First quantum stock price
Significant technological advancements within the quantum computing field can drastically impact stock prices. Announcements of breakthroughs in qubit stability, improved quantum algorithms, or the development of more powerful quantum computers can generate significant positive market reactions. Conversely, setbacks or delays in technological progress can lead to negative reactions.
Investor Speculation and Market Trends
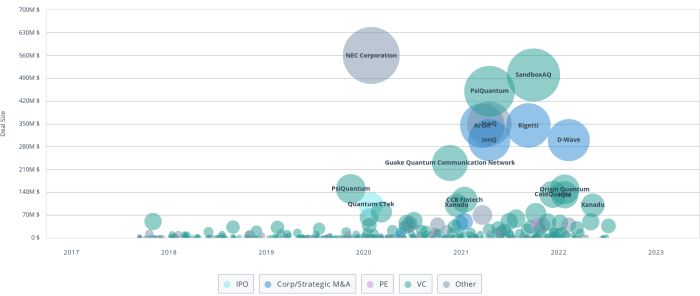
Source: thelephant.io
Investor speculation plays a significant role, particularly in emerging sectors like quantum computing. Hype cycles and market trends can lead to price fluctuations that may not always accurately reflect the underlying technological progress. Understanding these speculative dynamics is essential for making informed investment decisions.
Comparison with Other Technology Companies
Comparing the stock performance of quantum computing companies with those of other technology companies in related sectors (e.g., semiconductor companies, software companies) provides valuable context. This comparison helps to identify unique risks and opportunities associated with the quantum computing industry and assess the relative performance of quantum computing investments against more established technology sectors.
Future Projections and Predictions
Predicting future stock price movements for quantum computing companies involves considering various scenarios based on different assumptions regarding technological progress, market adoption, and macroeconomic conditions. These predictions are inherently uncertain but provide a framework for understanding potential future outcomes.
Potential Future Stock Price Movements
Several scenarios are possible. A bullish scenario assumes rapid technological advancement, significant market adoption, and favorable macroeconomic conditions, leading to substantial stock price appreciation. A bearish scenario assumes slower-than-expected progress, limited market adoption, and unfavorable economic conditions, resulting in stagnant or declining stock prices. A neutral scenario would represent a more moderate outlook, balancing potential positive and negative developments.
Visual Representation of Potential Trajectories
Imagine three lines representing stock price trajectories over time. The bullish scenario would show a steep upward trend, the bearish scenario a flat or downward trend, and the neutral scenario a more gradual upward trend with some fluctuations. The specific numbers would depend on the assumptions made for each scenario.
Underlying Assumptions
The accuracy of these projections relies heavily on the underlying assumptions. These assumptions might include the pace of technological development, the timing of market adoption, the competitive landscape, and macroeconomic factors. Different assumptions lead to different predicted outcomes, highlighting the uncertainty inherent in such projections. For example, a bullish scenario might assume the successful development of fault-tolerant quantum computers within the next 5-10 years, while a bearish scenario might assume significant technical hurdles and delays.
Investment Implications and Risks
Investing in quantum computing stocks presents both significant potential rewards and considerable risks. A careful assessment of the risk-reward profile is essential before making any investment decisions.
Potential Risks
The primary risks include technological uncertainty (the possibility of unforeseen technical challenges delaying progress), competitive pressures (the emergence of new players or unexpected technological breakthroughs from competitors), regulatory hurdles (potential changes in government regulations impacting the industry), and market volatility (the inherent risk associated with investing in a relatively young and rapidly evolving sector).
Potential Rewards and Returns
The potential rewards stem from the transformative potential of quantum computing across various industries. Successful quantum computing companies could achieve substantial market capitalization and deliver high returns for early investors. The potential for disruptive innovation and market dominance makes it an attractive but also high-risk investment proposition.
Risk-Reward Profile Comparison
Compared to more established investment options, quantum computing stocks present a higher-risk, higher-reward profile. The potential for exceptional returns is balanced by the substantial uncertainties and risks associated with the technology and the market. Investors should carefully consider their risk tolerance before allocating capital to this sector.
Key Investment Considerations
- Thorough due diligence on the company’s technology and business model.
- Assessment of the competitive landscape and potential disruptive technologies.
- Understanding the macroeconomic factors influencing the sector.
- Careful consideration of personal risk tolerance and investment goals.
- Diversification of investment portfolio to mitigate risk.
FAQ Summary
What are the ethical considerations of investing in quantum computing?
Ethical concerns surrounding quantum computing investments include potential misuse of the technology (e.g., cryptography breaking) and ensuring equitable access to its benefits. Investors should research the ethical practices of companies in this field.
How does government regulation impact quantum computing stocks?
Government policies and funding for quantum research significantly influence the sector’s growth and stability. Regulatory frameworks related to data privacy and national security can also affect stock prices.
What are the main competitors to the “first” quantum stock?
The competitive landscape in quantum computing is rapidly evolving, with numerous companies developing different quantum technologies. Identifying key competitors requires ongoing research into the field.